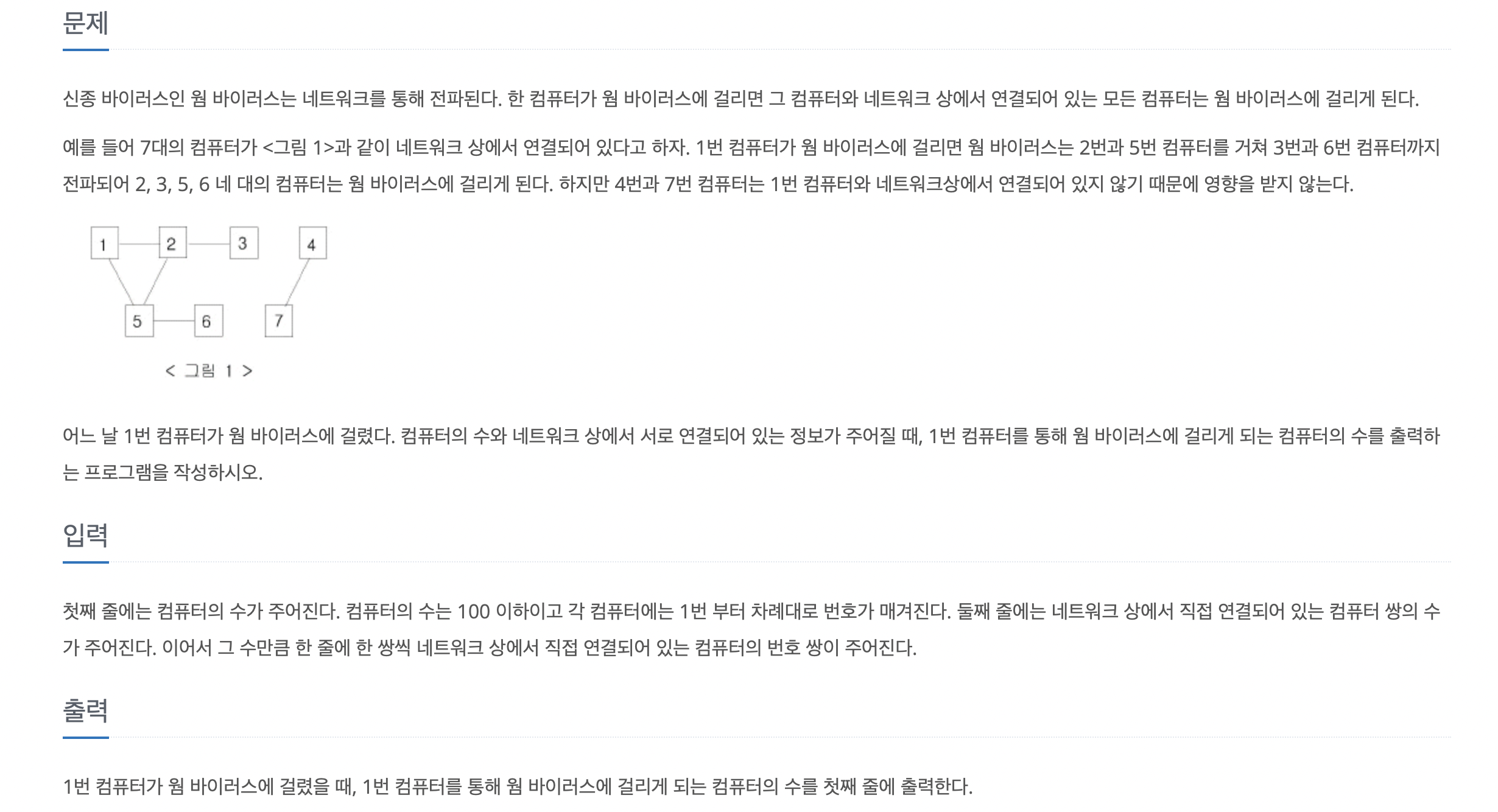
백준 바이러스(2606)
풀이
bfs, dfs 구현만 해주면 되는 문제
- bfs (너비 우선 탐색)을 통해 연결된 노드의 수 세주기
- dfs (깊이 우선 탐색)을 통해 연결된 노드의 수 세주기
아래 풀이는 bfs 방식으로 작성했습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class FastScanner {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastScanner() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
public class Main{
static int n;
static int m;
static boolean visited[];
static int count;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> computer;
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
FastScanner sc=new FastScanner();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
// 노드의 수, 정점의
n = sc.nextInt()+1;
m = sc.nextInt()+1;
computer = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
computer.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
// 양 방향 연결
for(int i=0; i<m-1; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
computer.get(v1).add(v2);
computer.get(v2).add(v1);
}
bfs();
bw.write(Integer.toString(count));
bw.close();
}
public static void bfs() {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited = new boolean[n];
queue.add(1);
visited[1] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tmp = queue.poll();
Iterator<Integer> it = computer.get(tmp).iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
int i = it.next();
if (!visited[i]) {
queue.add(i);
visited[i] = true;
count ++;
}
}
}
}
}
