특정 거리의 도시 찾기 (18352)
풀이
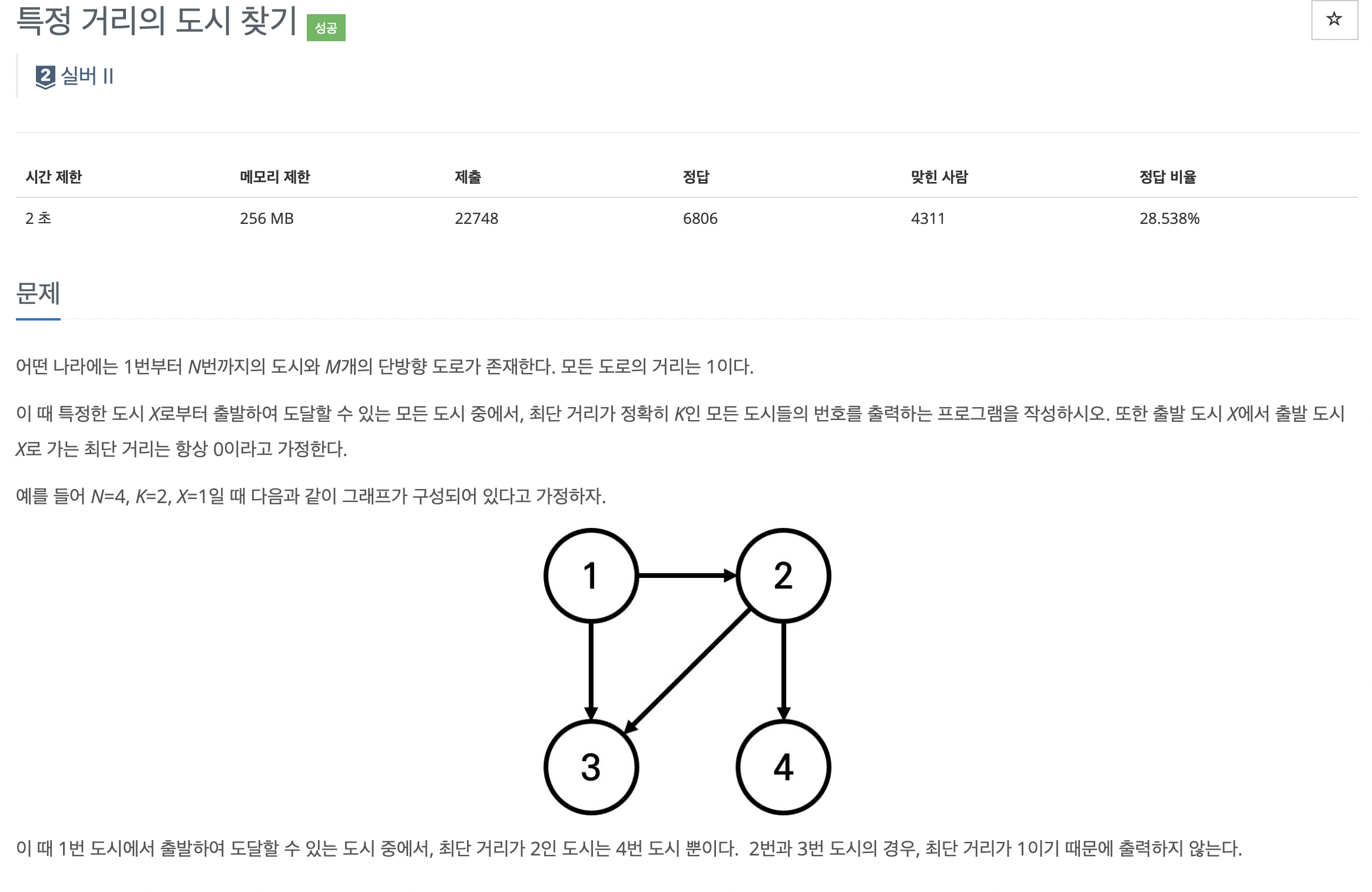
- 출발 노드 기준으로 bfs를 돌리면서 거리를 배열에 기록해주면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class FastScanner {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastScanner() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
}
public class Main {
static int n; // 정점 수
static int m; // 엣지 수
static int k; // 최소 거리
static int x; // 출발 정점
static ArrayList<Integer> list[];
static int dis[];
static boolean visited[];
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FastScanner sc = new FastScanner();
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
k = sc.nextInt();
x = sc.nextInt();
list = new ArrayList[n+1];
dis = new int[n+1];
visited = new boolean[n+1];
for(int i=0; i <= n; i++)
list[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
list[a].add(b);
}
bfs(x);
boolean isExist = false;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if(dis[i] == k) {
System.out.println(i);
isExist = true;
}
}
if(!isExist)
System.out.println("-1");
}
public static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(start);
visited[start] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int cur = queue.poll();
for(var next : list[cur]){
if(!visited[next]){
visited[next] = true;
queue.add(next);~~~~~~
dis[next] = dis[cur] +1;
}
}
}
}
}
